FE502 – Glossary
FE502 – GlossaryFinancial marketsSecurity (also called a financial instrument)BondInterest rateStock (common stock)The forex exchange market Financial intermediariesBanks MoneyAggregate output Unemployment rateBusiness cyclesRecessionsMonetary theoryAggregate Price Level (Price Level)InflationMonetary PolicyFiscal PolicyFiscal vs Monetary policyHow it worksGDP (Gross domestic product)Why importantReferences
Financial markets
markets in which, funds are transfered from people who have an excess of available funds to people who have a shortage.
Security (also called a financial instrument)
is a claim on the issuer’s future income or assets ( any financial claim or piece of property that is subject to ownership)
Bond
A bond is adebt security that promises to make payments periodically for a specified period of time. The bond market is espacially important to economic activity because it enables corporations or governments to borrow to finance their activities and because it is where interest rates are determined.
Interest rate
An interest rate is the cost of borrowing or the price paid for the rental of funds (usually expressed as a percentage of the rental of 100$ per year)
Because changes in interest rates have important effects on individuals, financial institutions, businesses, and over all economy, it is important to explain fluctuations in interest rates that have been substantial over the past twenty years1.
One way that interest rates matter is they influence borrowing costs and spending decisions of households and businesses[4].
Lower interest rates, for example, would encourage more people to obtain a mortgage for a new home or to borrow money for an automobile or for home improvement. Lower rates also would encourage businesses to borrow funds to invest in expansion such as purchasing new equipment, updating plants, or hiring more workers. Higher interest rates would restrain such borrowing by consumers and businesses.
The Fed seeks to set interest rates to help set the backdrop for promoting the conditions that achieve the mandate set by the Congress--namely, maximum sustainable employment, low and stable inflation, and moderate long-term interest rates[4].
United States Fed Funds Rate (US Interest Rate)
TR interest rates
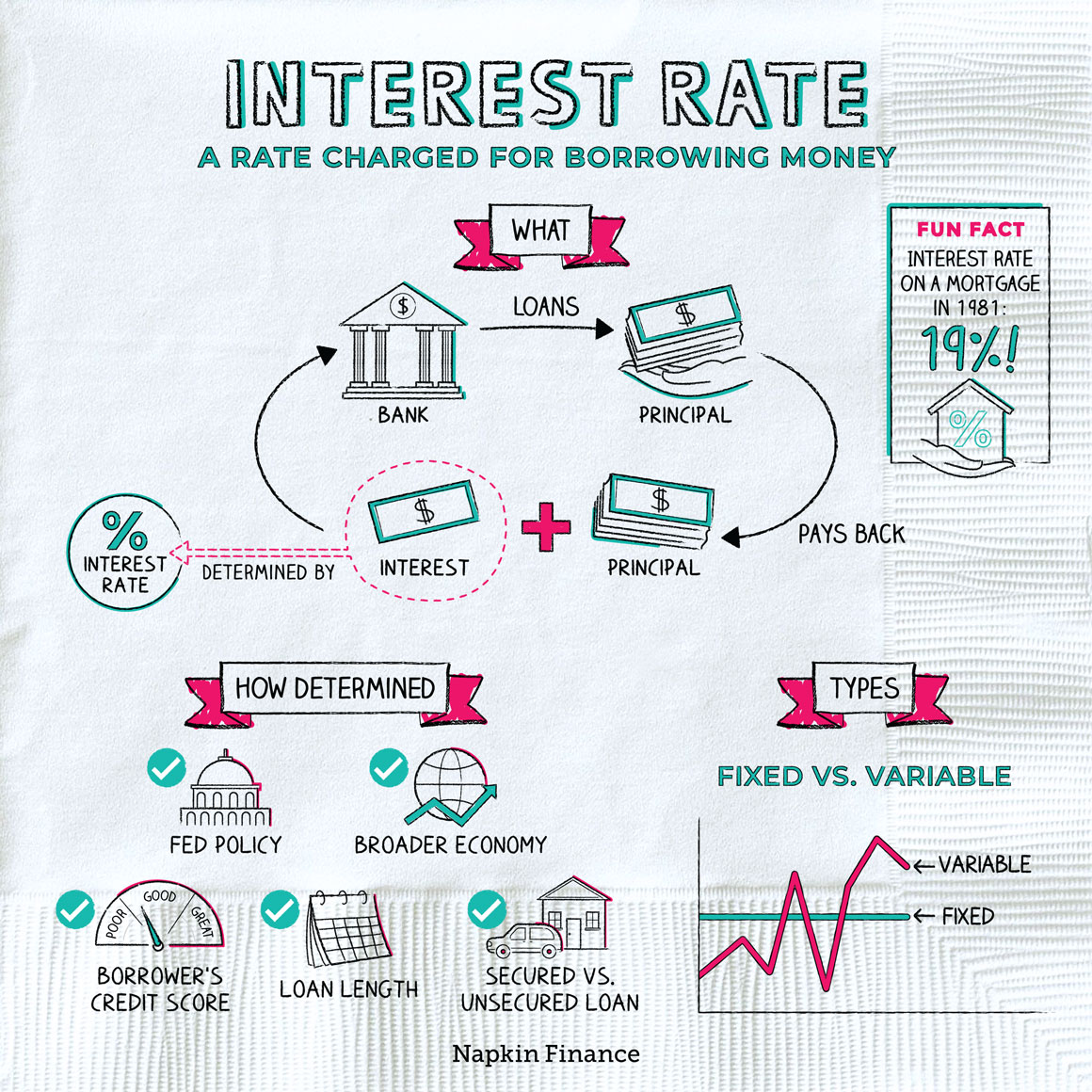
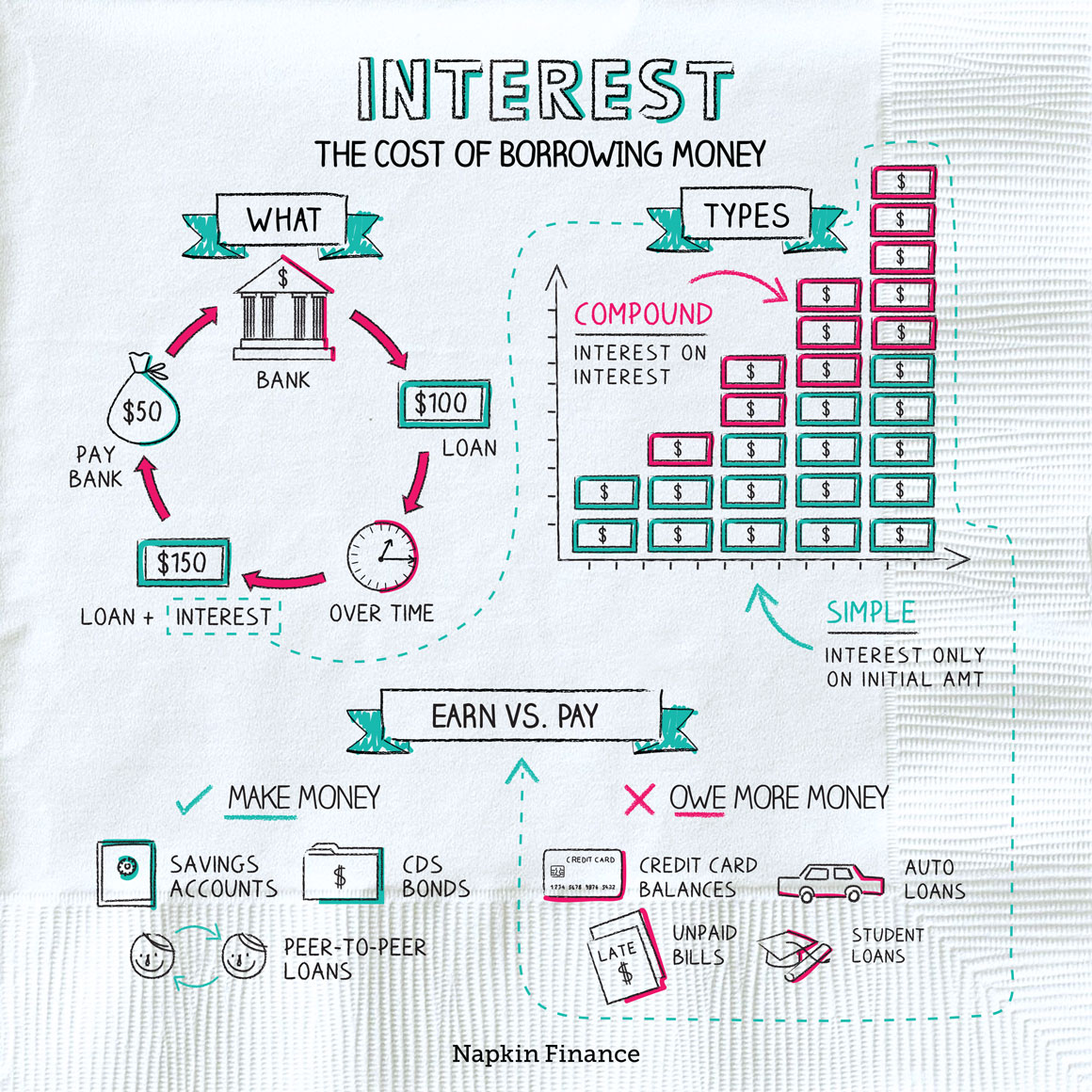
Fun facts [1] [2]
- Although it’s rare, interest rates can be negative—with the bank paying you to take out a loan (or charging you to keep your money safe).
- Islamic law prohibits paying or receiving interest. If you open a savings account with a Sharia-compliant bank, you may be offered a “target profit” instead of an interest rate.
Key takeaways
- Interest is the cost of borrowing money.
- If you’re borrowing money, interest works against you. If you’re lending money, interest works for you.
- If you’re ever comparing interest rates, make sure you’re comparing the same type of rate.
- Compound interest helps when you’re lending but hurts when you’re carrying a balance.
Stock (common stock)
A common stock represents a share of ownership in a corporation. It is a security that is a claim on the earnings and assets of the corporation. Issuing stock and selling it to the public is a way for corporations to raise funds to finance their activities.
Why invest in stocks
People invest in stocks because they hope to earn a better return on their money than they could with a safer alternative, such as a savings account. Investors can earn returns on stocks in two main ways:
- Price gains—If you buy a stock when the share price is
- Dividends—Some companies pay out a portion of profits to their shareholders in the form of cash dividends. If you own a stock with a price of
Types
There are thousands upon thousands of stocks you can choose from, and they’re generally sorted into a handful of categories, including:
Com
mon vs. preferred
- Common stocks—what people really mean when they talk about “stocks.”
- Preferred stocks—technically also stocks but really a different beast entirely. Preferred stocks generally pay high fixed dividend rates and don’t swing in value the way common stocks do. They’re stocks that act almost like bonds.
Domestic vs. international
- Domestic stocks—issued by companies based in the U.S. (or an investor’s home country) though many U.S. companies do business all around the globe.
- International stocks—issued by companies headquartered elsewhere.
Growth vs. value
- Growth stocks—issued by companies with rapidly growing sales and/or profits. (Any investor who’s hoping to find the “next Facebook” is probably focusing on growth stocks.)
- Value stocks—stocks that are selling “cheaply” compared with the underlying company’s profits.
Large cap vs. small cap
- Large cap stocks—issued by companies with a market capitalization of $10 billion or more.
- Small cap stocks—issued by companies with a market capitalization of $2 billion or less. (There are also micro, mid, and mega capitalization stocks.)
Sector or industry
- There are various sector and industry classifications based on what a company does, including energy, technology, healthcare, and utilities.
The forex exchange market
For funds to be transfered from one country to another, they have to be converted from the currency in the country of origin (say, dollars) in to the currency of the country they are going to (say, euros). The foreign exchange market is where this conversion takes place, and so it is instrumental in moving funds between countries. It is also important because it is where the foreign exchange rate, the price of one country’s currency in terms of another’s, is determined.

The foreign exchange, or forex, markets are where investors go to buy and sell currencies. [6]
Unlike the stock market, where investors buy and sell investments through an exchange, forex trading is called an “over-the-counter” (OTC) market. That means it’s made up of an informal network of buyers and sellers, with investors typically making trades through a dealer.
A wide range of players trade in the forex market, including:
Governments
- Central banks or other government entities may trade currencies to try to influence the price of their home country’s currency or to smooth out bumps in its price changes.
Dealers
- Large financial institutions make currency trades for their clients and may enter into their own trades as well.
Corporations
- If a company sells goods in the U.S. but is based in Germany, it may need to convert the U.S. dollars it receives into euros. That means going through the forex market.
Investors
- Large investors and small investors may make bets on currency price movements or may need to exchange currencies in order to make an investment in another country.
Individuals
- If you go on vacation or a work trip to another country and need to exchange currency when you arrive (or leave), you’re going through the forex market too.
What drives prices
Currency price movements can be driven by:
- Interest rates: Higher interest rates often drive a country’s currency up.
- Inflation: Higher inflation typically makes a currency fall.
- Economic growth: Higher economic growth tends to attract investors into a country, which makes its currency rise.
A change in the exchange rate has a direct effect on American consumers because it affects the cost of imports. Foreign currency rises, your desire to go to that foreign country to vocation is drops, and your desire to buy that foreign country’s goods also drops.
Domestic currency weakeness — > import becomes less/
Financial intermediaries
Institutions that borrow funds from people who have saved and in turn make loans to others.
Banks
Banks are financial institutions that accept deposits and make loans.
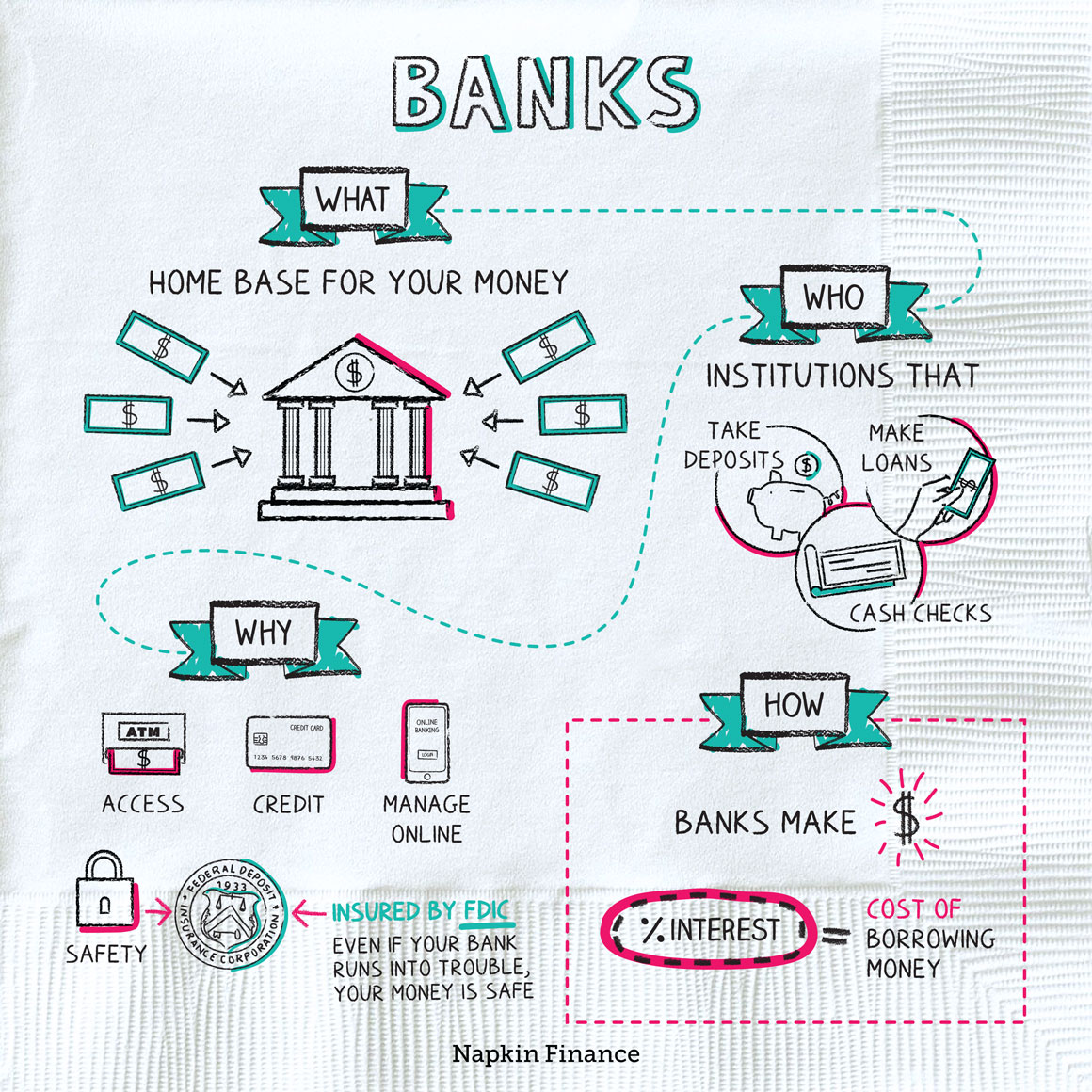

Bank services [7]
Banks offer various products and services to their customers, including:
- Checking accounts: A checking account lets you deposit your paycheck or withdraw money easily for short-term spending.
- Savings accounts: Savings accounts are better suited for money you’ll hold at the bank for a longer term. They can protect your money and help you increase your wealth as you earn interest.
- Credit cards: Allow you to purchase everyday items or pay certain bills conveniently using borrowed money. You pay interest on what you borrow and have to make monthly payments to avoid fees.
- Loans: These include mortgages, auto loans, business loans, and personal loans that you pay back in installments over a set period of time.
Depending on the bank, you can access services in person at a branch, over the phone, online, or through an app.
Banks make loans to people and companies and charge interest on those loans (they also make money if you trigger fees on your account, although for most banks that’s not their main source of income).
Because they receive that interest income, banks are generally also able to pay a small amount of interest on money held in savings accounts.
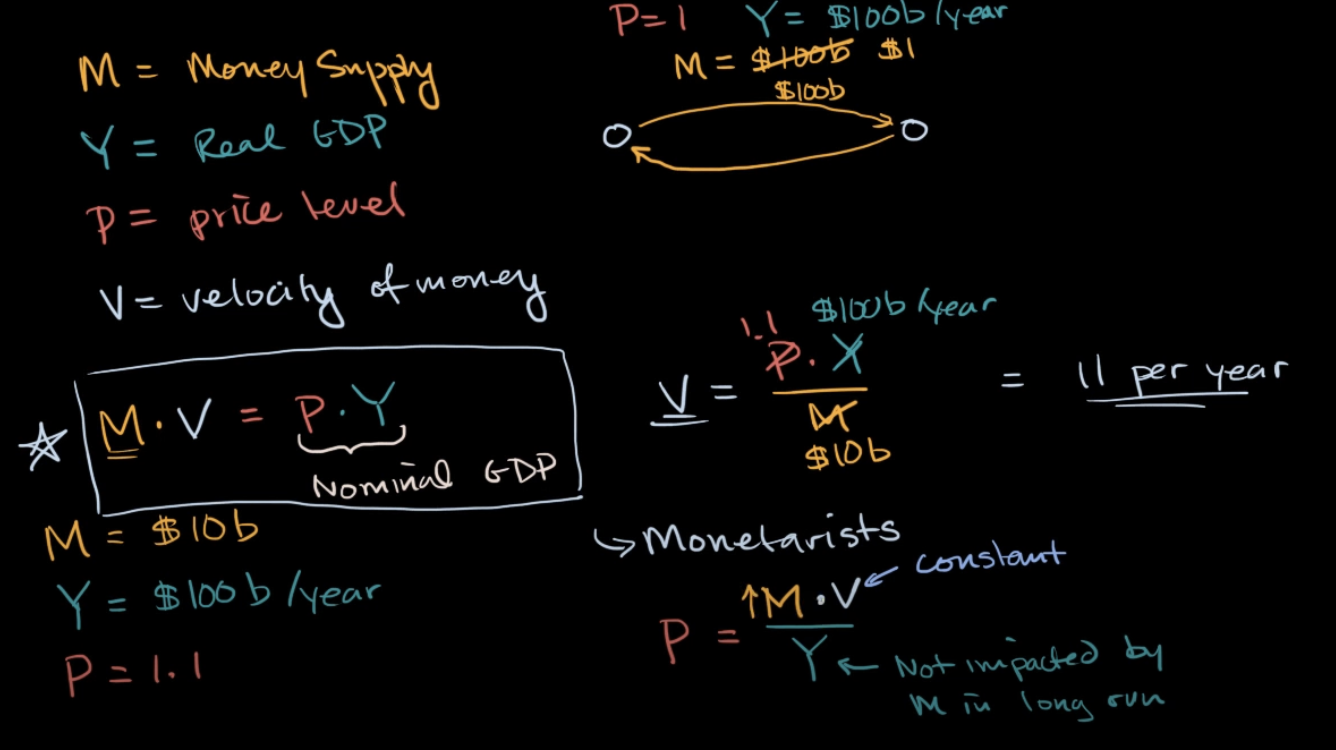
Money
Money, also referred to as the money supply, is defined as anything that is generally accepted in payment for goods or services or in the repayment of debts.
Video source: Khan Academy [8]
Aggregate output
The total production of goods and services.
Decrease in aggregate output will increase the unemployment rate.
Unemployment rate
The percentage of the abailvable labor force unemployed.
Business cycles
The upward and downward movement of aggregate output produced in the economy.
Recessions
Periods of declining aggregate output.
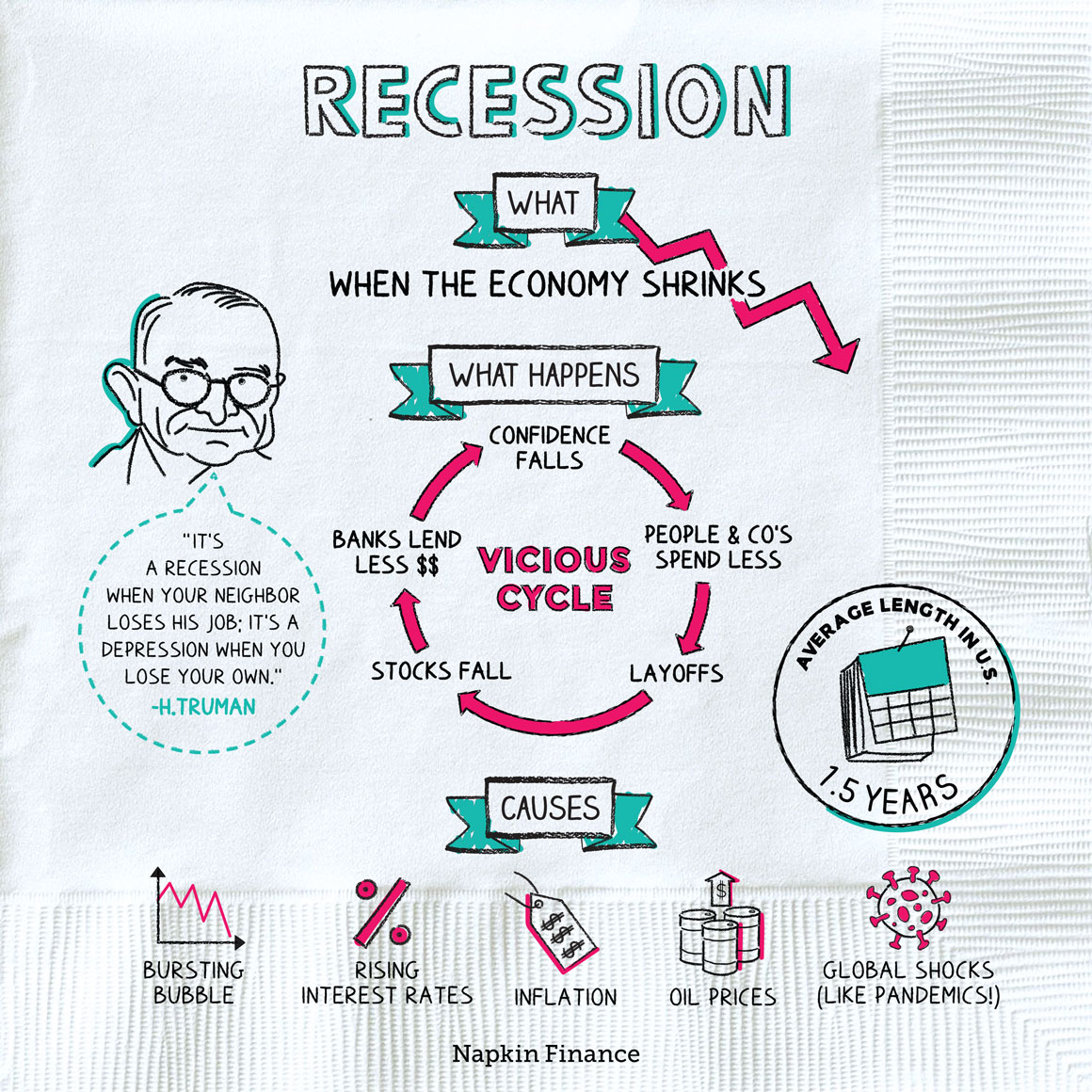
Feel the Pinch[9].
A recession refers to a time when the economy shrinks instead of grows. More specifically, economists typically define it as a time when GDP falls for at least two consecutive quarters.
What happens?
Recessions are economic downward spirals. Sometimes they can be fairly mild, and the economy (potentially with the help of the government) rights itself after only a few months. Sometimes they can be extreme. Here’s how a recession typically plays out:
- Confidence declines—People and businesses start to worry about the economy. Since they’re worried, they spend less money.
- Profits fall—As people and companies spend less, corporate profits fall or turn into losses.
- Workers lose their jobs—With profits falling, companies try to cut costs. That means layoffs.
- Stocks fall—If companies are earning less money, then their stocks are worth less. Falling stocks compound the problem—people and companies feel less rich (because their investments are worth less), meaning they spend even less money.
- Banks lend less money—With the economy heading south, banks start to worry that loans they make won’t be paid back. Reduced lending also compounds the problem.
Causes
Recessions are complicated, and even experts disagree about their exact causes. Some causes that are at least partly to blame may include:
Bursting bubbles
- If a particular investment shoots way up in price—beyond what it’s truly worth—then it’s called a bubble. When the bubble pops, the investment’s price falls fast and may pull other prices down with it.
Rising interest rates
- Higher interest rates hit the brakes on the economy.
Inflation
- Very high inflation makes it hard for the economy to run smoothly.
Oil prices
- Several historical recessions were at least partly caused by sudden spikes in the price of oil.
Events out of left field
- In April 2019, no one had the phrase “coronavirus pandemic” on their mind. By April 2020, it had thrown the world economy into a deep recession.
Recession vs. depression
Recessions and depressions are both times of economic decline, but they differ in their severity and timing.
- Recession: A downturn that lasts months or possibly as long as a few years. Often, only one or two industries feel the worst of it. It’s painful but not catastrophic for most people.
- Depression: Starts as a recession but is longer and worse. It touches almost every part of the economy and daily life. It can be economically catastrophic for lots of people.

Monetary theory
The theory that relates changes in the quantity of money to change in aggregate economic activity and the price level.
Aggregate Price Level (Price Level)
The avarage price of goods and services in an economy is called the aggregate price level.
Inflation
Inflation, is a continual increase in the price level, affects individuals, businesses, and the government.
A continues increase in the money suplly might be an important factor in causing the continuing increase in the price level that we call inflation.
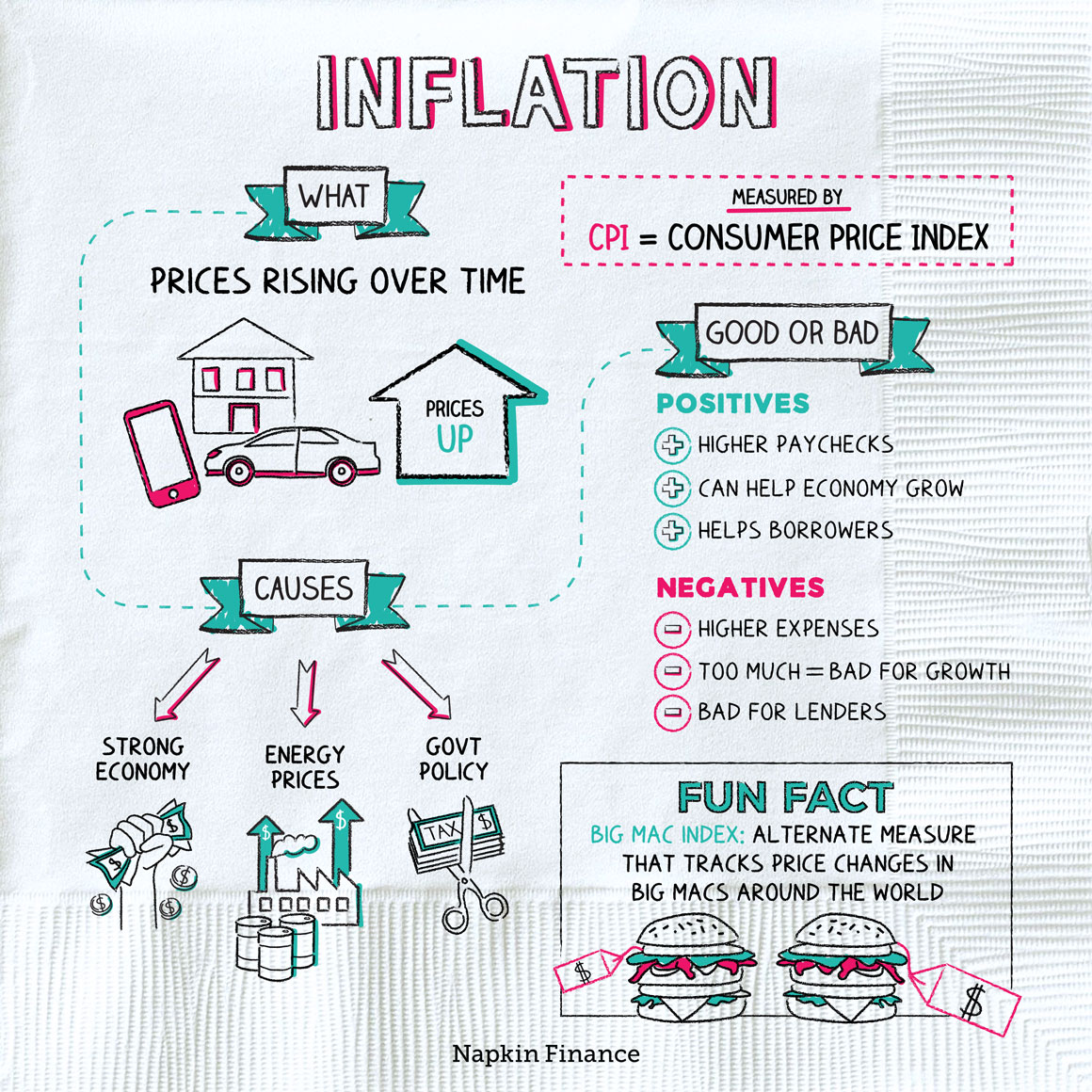
Why it happens
Many different factors can contribute to inflation, including:
- A booming economy—Economic growth usually goes hand in hand with at least some inflation. If a company’s profits are good, it may give more raises to employees. If people are feeling secure in their jobs, they’re probably spending more money. The more they spend, the more prices tend to go up.
- Energy prices—The economy depends on oil and other energy sources in a variety of ways. When the cost of energy goes up, the cost of making goods, shipping goods, and keeping the lights on at stores goes up too. That means prices of goods and services tend to rise as well.
- Government policy—If the government cuts taxes, lowers interest rates, or prints money, both economic growth and inflation typically get a boost.

Inflation sucks because it means everyone is rich but nobody can afford anything. — Napkin Finance
Monetary Policy
The managment of money and the interest rate.
The organization responsible for the conduct of a nation’s monetary policy is the central bank. in the US it is FED.
Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy evolves decisions about government spending and taxation.
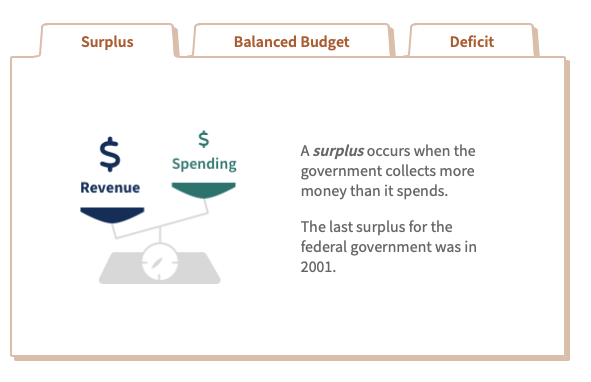
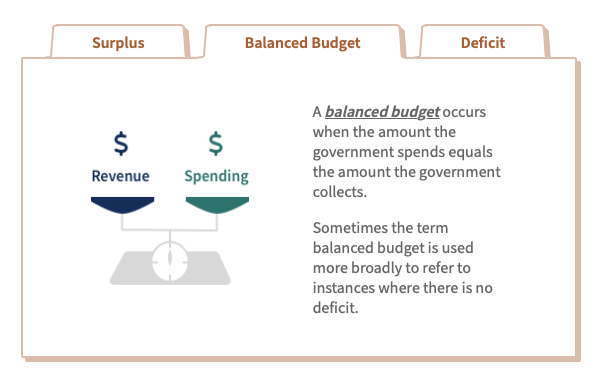
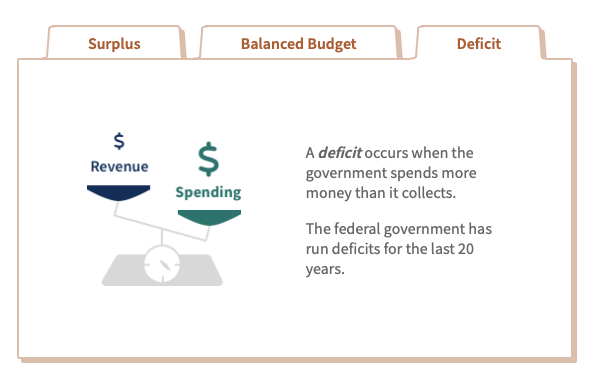
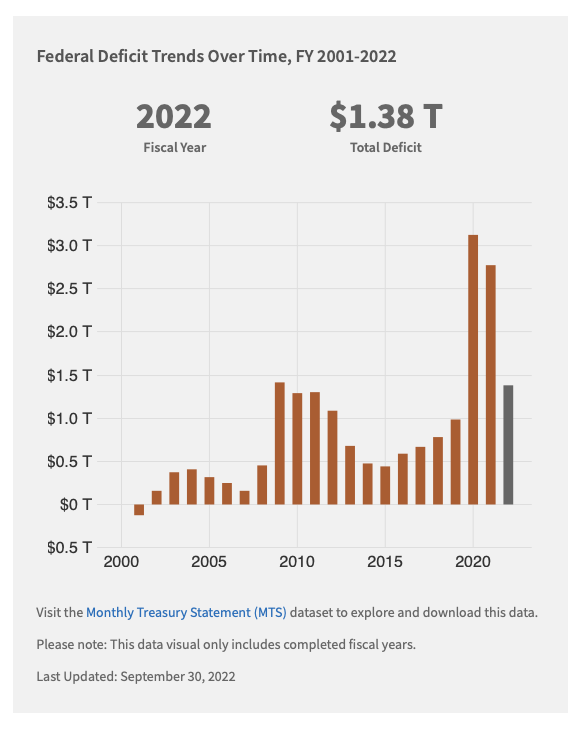
A budget deficit is the excess of government expenditures over tax revenues for a particular time period, typically a year.
A budget surplus arises when tax revenes exceded government expenditures.
The goverment must finance any deficit by borrowing, while a budget surplus leads to a lower government debt burden.
Fiscal vs Monetary policy
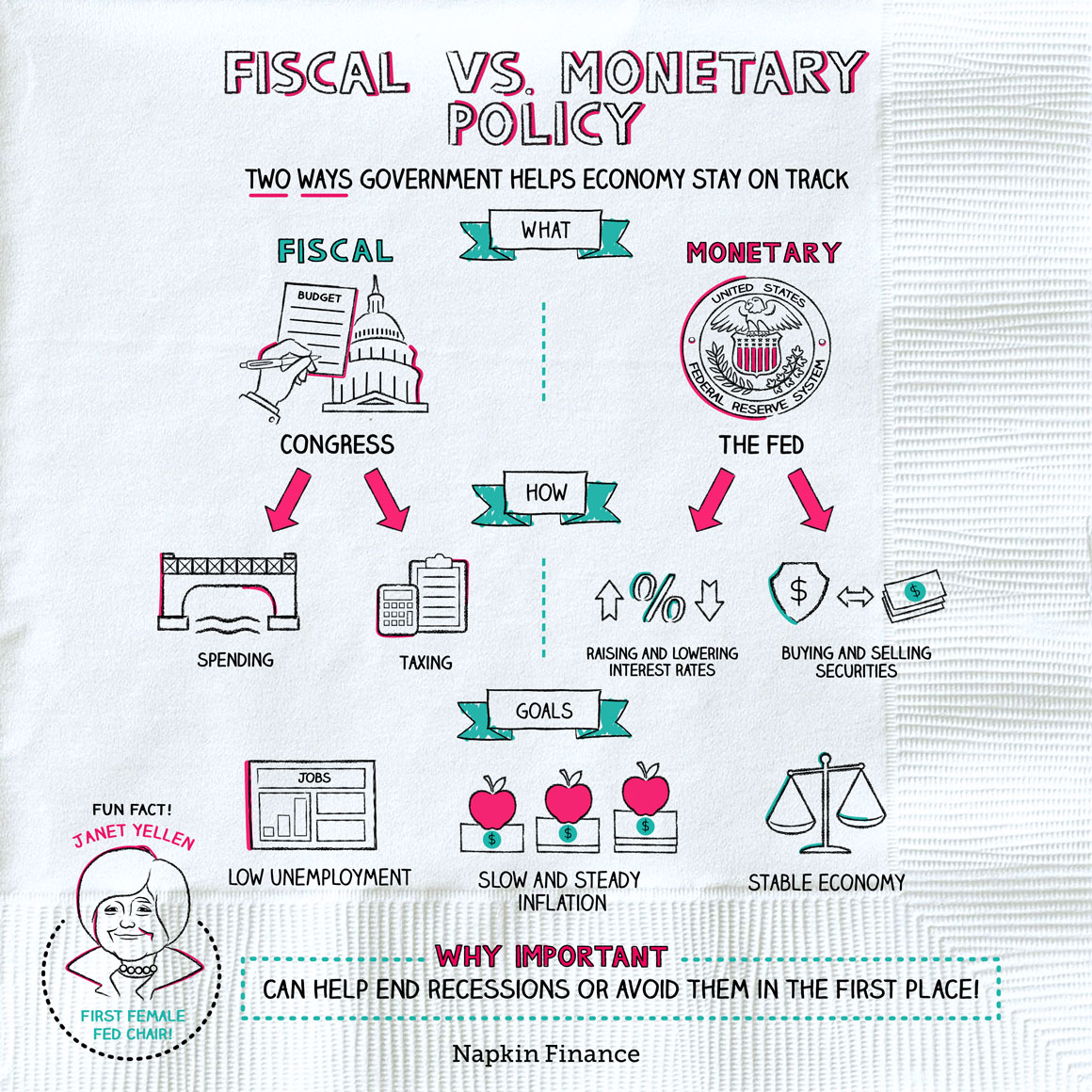
Fiscal policy describes the government’s decisions on whom it taxes (and how much) and where it spends its money.
Monetary policy describes actions taken by the Fed.
| Fiscal policy | Monetary policy | |
|---|---|---|
| Who controls | Congress (with the president’s OK) | The Fed |
| Goals | Low unemploymentSlow-but-steady inflationEconomic growth | Low unemploymentSlow-but-steady inflation |
| How achieves | Taxing and spending | Main tool: Raising and lowering interest rates Other tools: Buying and selling investments; changing reserve requirements (how much extra cash banks have to keep on hand) |
The government helped pull the U.S. economy out of the Great Depression through heavy spending on public works projects (i.e., through fiscal policy). And the Fed helped ease the Great Recession by lowering interest rates and buying securities (i.e., through monetary policy).
How it works
Suppose economic growth is slowing down and experts are worried the economy is heading into a recession. Either (or both) monetary or fiscal policy could be used to help boost growth:
| Fiscal | Monetary |
|---|---|
| Congress cuts taxes (or increases spending) ↓ People and companies pay less to the government in taxes (or they receive more from government spending) ↓ People and companies have more money to spend ↓ Economy grows faster | The Fed lowers interest rates ↓ Loans are cheaper, so people and businesses borrow more money ↓ People and companies have more money to spend ↓ Economy grows faster |
suppose the economy is growing very quickly and experts are worried about rising inflation (which can make the economy unstable).
| Fiscal | Monetary |
|---|---|
| Congress raises taxes (or reduces spending) ↓ People and companies pay more to the government in taxes (or they receive less from government spending) ↓ People and companies have less money to spend ↓ Economy slows | The Fed raises interest rates ↓ Loans are more expensive, so people and businesses borrow less money ↓ People and companies have less money to spend ↓ Economy slows |
GDP (Gross domestic product)

GDP: is a measure. of aggregate output.
Gross domestic product, or GDP, measures the size of an economy. In essence, it puts a dollar figure on all the goods and services that a country produces in a given year (or other period).
Why important
Tracking a country’s GDP tells us two things:
- The overall size of the country’s economy
- Whether the economy is growing or shrinking and at what rate
